Site Map FAQ Link Contact About
Electric Bicycle Motor Mounting Positions
There are a couple of configuration that are used to mount the the electric bicycle motor onto the bicycle, each one has it's benefit and shortcomings. I will cover all of them and try to emphasize the key difference between them.
Also, it is good to know that each one of those configurations can be connected to almost any type of bicycles, but there are exceptions. The bicycle’s front fork can be an obstacle, for example, for installing some of the electric bicycle motors that are designed to be located at the hub of the front wheel.
A list of electric bicycle motor mounting positions:
Front Wheel Drive
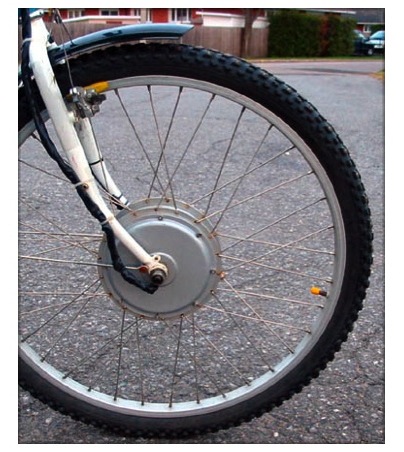

The front wheel drive motor is built into the center of the front wheel. It is basically isolated from the rest of the bicycle and therefore pretty simple and adaptable.
The rear gearing system stays untouched, it is a big plus for bicycles with rear internal gear hubs. It leaves the bicycle with full rear hub options for derailleur or hub gears, it is not set any special constraints.
Many conversion kits use this kind of configuration. It is very simple and straightforward to install. Just replace the old wheel with a new wheel that include the electric bicycle motor and you are almost done.
Assuming the battery is located at the rear of the bike, you get a better weight distribution (as opposed to a typical front wheel drive).
Also, practically you get a two wheel drive (rear wheel pedaling and front wheel motor assistance). A two wheel drive is better for use on slippery surface because you get better handling (Just like a four wheel drive automobile). Another thing is that the front wheel motor assistance won't cause any unintended wheelies on sudden acceleration.
But of course, nothing is perfect, and the front wheel drive also has some disadvantages.
The additional weight of the front wheel can cause the ride to be less comfort on uneven roads because the added weight create more force on the handlebars when going over a bump.
Some say that in the real world the added weight is hardly noticed. You only notice it when you have to lift the front wheel. My opinion is that each front wheel drive design act a little differently.
There is more pressure on the front fork. This kind of motor configuration is usually not suitable for aluminum forks which is the preferable material from a weight point of view (vs. steel forks). The electric bicycle motor is just too powerful for an aluminum fork and can bend or even break the drop-outs.
A front motor can also cause slight uncomfortable steering behavior because of the added weight, especially at low speeds and also some front frame vibration. The front drive also has decreased traction in wet condition and off road riding in comparison to some other drive systems.
In comparison with other drive systems which use the bicycle gears (e.g chain drive), the front wheel has no gears. Therefore, in order to produce the same output power, a bigger front wheel motor is required in comparison with a chain drive motor. A bigger motor weigh more and gobble more energy
Rear Wheel Drive

It has good balancing and traction in wet conditions and for an off road rides because of this rear drive propulsion.
On the other hand, there is a considerable increase of weight in the back of the bicycle (if the battery is mounted on the rear rack). This can cause more stress on the rear wheel and imbalance.
Also, the rear electric bicycle motor assistance is prone to unintended wheelies on sudden acceleration.
Some rear wheel drive systems have a limitation for the maximum number of speed freewheel. Also, rear motors can't use a cassette gear system and have to use a weaker multi-sprocket freewheels which have much less choice of sprockets.
Like the front wheel drive, in comparison with other drive systems which use the bicycle gears (e.g chain drive), the rear wheel has no gears.
Chain Drive

A bicycle is the most efficient mode of transportation on Earth because of the gearing system. The chain drive configuration has the electric bicycle motor mounted near the crank and power the bicycle through the pedal gears (drive train).
A chain drive also known as mid drive, crank drive, shaft drive or motorized bottom brackets drive.
The connection through the pedal gears has better torque in comparison with the front/rear wheel drive. It has better hill climbing ability and it's better for pulling heavy loads by using the electric assist in the lower gears of the bike.
The electric bicycle motor location is very close to the ground so the center of gravity is also very low. Some motors are sealed and protected so there should be no fear of jumping on sidewalks, riding over rocks,etc but there are motors which are not protected and therefore requires more gentle style of riding.
Some systems integrates the motor to the already exist chain of the bicycle, while other connect the motor to the bicycle using an additional chain.
This kind of system typically make more noise compared to other configurations because of the integration with the chain.
The connection of the motor through the chain add friction. Therefore, when pedaling you will have to overcome the added friction of the motor.
Unsealed chain drive systems usually looks less "elegant" compared to other drive systems. The look is just not "clean" enough. A lot of DIY electric bicycles are built this way. But the sealed and protected systems usually have a very "integrated" and clean look.
 |
 |
Friction Drive

This is probably one of the first types of electric propulsion that were used for propelling electric bicycles. A shaft extends from the motor and it is in contact with the front or rear wheel. The bike moves forward when the shaft turns. It is that simple!
On one hand we have a very simple and quite cheap drive system, but on the other hand there are a lot of disadvantages.
The difference between the shaft radius and the a wheel radius is big. In order to compensate on this difference, the motor has to spin really fast and motors efficiencies at high spin rates are low.
Moreover, the contact between the wheel and the electric bicycle motor is not ideal. The efficiency of energy transfer from the motor shaft to the wheel is low and external conditions such as tire pressure and a wet wheel can decrease the contact איכות even more.
Another shortcoming of this contact between the wheel and the motor shaft is that the tire wear out much quicker then usual because of the intense friction.
You won't reach high speed with this kind of drive system and you won't get a good torque. Plus, because of all the inefficiencies the energy consumption is high and therefore draining the battery faster in comparison with other systems.
But if all you need is a way to travel for short distances and you are also on a tight budget, I would still considering this option.
Push Trailer

The idea behind this drive system is quite unique. I never saw one in action, mainly because of the fact that, as far as I know, there is no even one commercial system like this.
What is so unique about it?
The propulsion system isn’t located on the bicycle but on a separated trailer. The electric bicycle motor and the battery are mount on the trailer while the controller can either be on the bike or on the trailer. The only part that must be on the bicycle is the throttle.
Therefore, the only installation required on the bicycle itself is sliding the throttle on the handlebar. Then you attach the trailer to the back of the bicycle and you are ready to go.
The connection and the disconnection of the trailer to the bicycle should be simple and quick.
At first glance, it may seem that it has no real use. But think about the possibility of having some kind of renting program. You can buy small amount of push-trailers and rent them to people with bicycles.
Moreover, if you have more then one pair of bicycle, you can purchase one push-trailer and connect it to the bicycle that you are going to ride on.
The bicycle stayed untouched (except the throttle), so if you want to go for a ride without the electric components, all you need to do is disconnect the trailer. In other system, the maximum that you can do is remove the battery. Removing the motor is usually not something that you would tend to do often (if possible at all).
But of course, not everything is gold. The one big disadvantage is that the “length” of the bicycle is much more compared to ordinary electric bike. Also, I don't have any data about the efficiency of this kind of drive system but pushing the bicycles from behind isn’t sound like such a good idea from an efficiency perspective.
Return from Electric Bicycle Motor Mounting Position to Electric Bicycle Structure
|








New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.